[문제 1]
1증가하는 코딩을 하세요
1) n = n + 1 ;
2) n += 1;
3) n++;
4) ++n;
[문제 2]
package days03;
public class Ex08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Type mismatch: cannot convert from double to float
// float pi = 3.141592;
float pi = 3.141592f; // 혹은 float pi = 3.141592F; 혹은 float pi = (float)3.141592;
// 소수점 4번째 자리에서 반올림한 실수값을 얻어와서 출력... 3.142
System.out.printf("%.3f\n", pi);
// [방법 1] 소수점 4번째 자리에서 반올림한 실수값을 pi에 저장
String.format("%.3f\n", pi); // "3.142"
pi = Float.parseFloat(String.format("%.3f", pi));
System.out.println(pi);
// [방법 2] 소수점 4번째 자리에서 절삭한 실수값을 얻어와서 출력...
System.out.println( pi * 1000 + 0.5 ); // 3142.092041015625
System.out.println( (int)(pi * 1000 + 0.5) ); // 3142
System.out.println( (int)(pi * 1000 + 0.5) / 1000f ); // 3.142
}//main
}//class
[문제 3]
public class Ex09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//The value of the local variable name2 is not used
// 선언했는데 왜 사용 안하니?
String name1 = "홍길동", name2;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("> 비교할 이름을 입력? ");
name2 = scanner.next();
// 디버깅
System.out.printf("[%s]\n", name2);
// == 연산자는 주소를 비교하기 때문에 false를 반환
// System.out.println( name1 == name2 );
// 따라서 object 클래스에 있는 equals()을 오버라이딩하여 사용해야함
// (암기) 두 문자열을 비교할 때는 equals() 사용한다.
System.out.println( name1.equals(name2) );
// 대소문자를 구분하지 않고 문자열 비교하는 함수 equalsIgnoreCase()
System.out.println( name1.equalsIgnoreCase(name2) );
System.out.println( "Heejin".equalsIgnoreCase("heejiN") );
}//main
}//class
[문제 4]
1) x는 10보다 크다
x > 10;
2) x는 10보다 크고 20보다 작다.
x > 10 && x < 20
3) x는 2의 배수이다.
x%2 == 0
4) x는 2의 배수 또는 3의 배수이다.
(x%2 == 0) || (x%3 == 0)
5) x는 2의 배수이지만 6의 배수는 아니다.
(x%2 == 0) && (x%6 != 0)
(x%2 == 0) && !(x%6 == 0)
6) 한 문자(ch)가 숫자이다.
'0' <= ch && ch <= '9'
48 <= ch && ch <= 57
7) 한 문자가 소문자이다.
'a' <= ch && ch <= 'z'
97 <= ch && ch <= 120
8) 한 문자가 알파벳(대문자이거나 또는 소문자)이다.
('A' <= ch && ch <= 'Z') || ('a' <= ch && ch <= 'z')
[문제 5]
public class Ex12 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 이름, 국어, 영어, 수학을 입력받아서
// 총점, 평균을 계산하고
// [출력형식]
// 홍길동님은 국어: 89 영어: 78 수학: 56 총점: 000 평균:00.00 이다.
String name;
int kor, eng, mat;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// 홍길동,90,78,99 엔터
System.out.print("> 이름,국어,영어,수학 입력? ");
String inputData = br.readLine();
// System.out.println(inputData); // "홍길동,90,78,99"
// "홍길동" "90" "78" "99" 구분자 콤마(,) 잘라내기
// 1) 기능 2) 매개변수 3) 리턴값(리턴자료형)
String [] datas = inputData.split(",");
name = datas[0];
kor = Integer.parseInt(datas[1]);
eng = Integer.parseInt(datas[2]);
mat = Integer.parseInt(datas[3]);
int total = kor + eng + mat;
double avg = (double)total/3;
System.out.printf("%s님은 국어: %d 영어: %d 수학: %d 총점: %d 평균:%.2f 이다.", name, kor, eng, mat, total, avg);
}//main
}//class
---
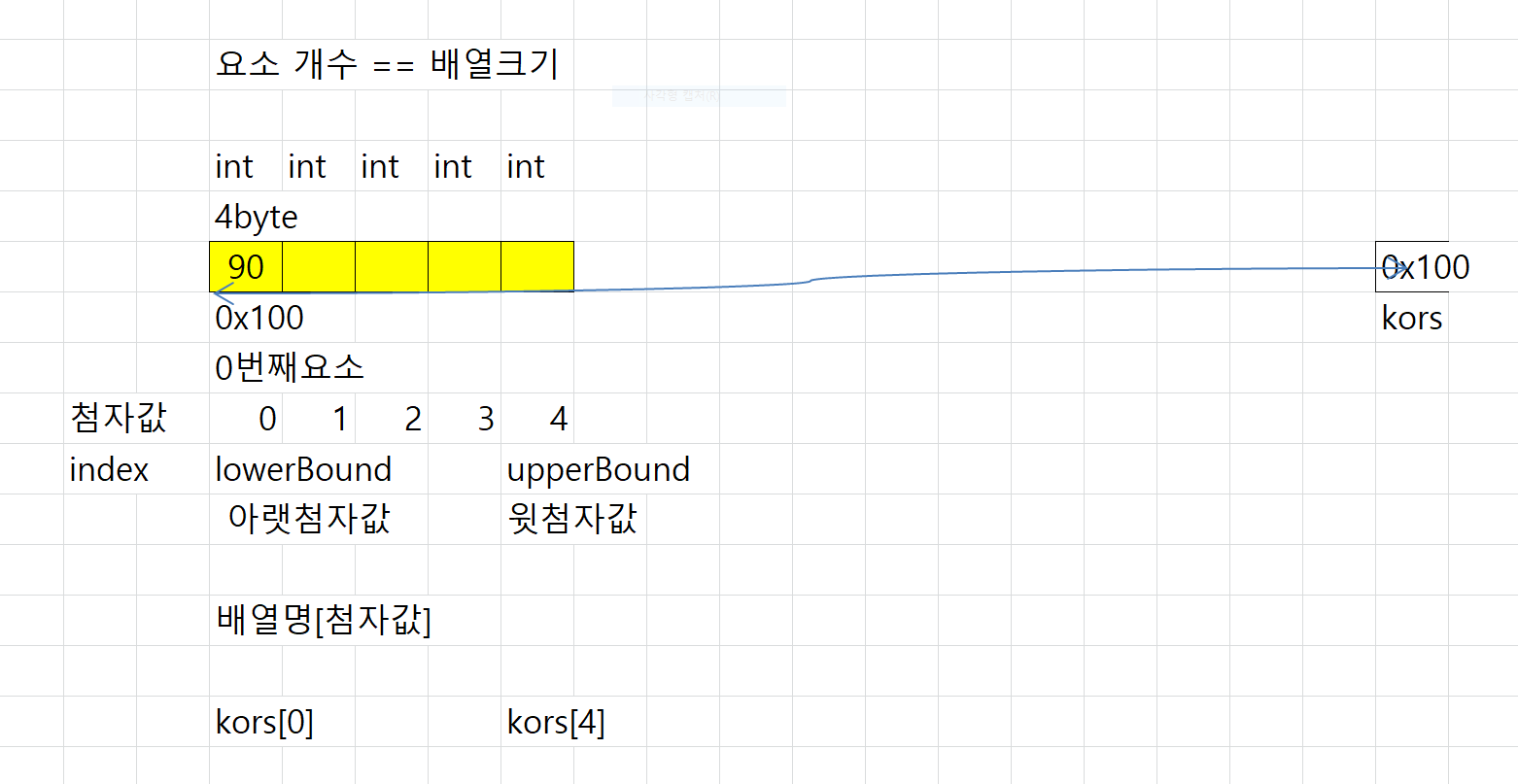
[참고] 수업자료
'Back-End > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ JAVA ] day05 Quiz (0) | 2023.07.19 |
|---|---|
| [ JAVA ] Day04 Quiz (0) | 2023.07.19 |
| [ JAVA ] Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero (0) | 2023.07.17 |
| [ JAVA ] 자료 형변환 (0) | 2023.07.14 |
| [ JAVA ] BigInteger, BigDecimal - long와 double 보다 더 큰 값을 갖는 자료형 (0) | 2023.07.14 |